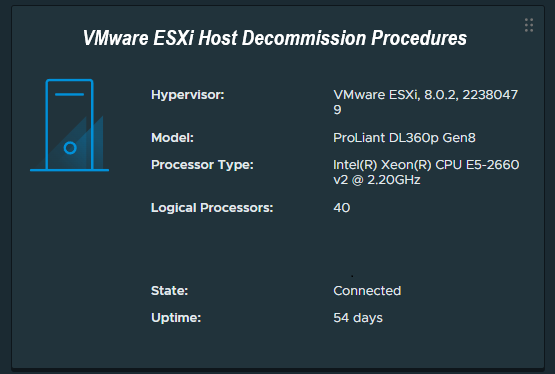
While most of us frequently deploy new ESXi hosts, a question and task not oftenly discussed is how to properly decommission a VMware ESXi host.
Some might be surprised to learn that you cannot simply just power down and remove the host from the vCenter server, as there are a number of steps that must be taken beforehand to ensure a proper successful decommission. Properly decommissioning the ESXi host avoids orphaned objects in the vCenter database, which can sometimes cause problems in the future.
Today we’ll go over how to properly decommission a VMware ESXi host in an environment with VMware vCenter Server.
The Process – How to decommission ESXi
We will detail the process and considerations to decommission an ESXi host. We will assume that you have since migrated all your VMs, templates, and files from the host, and it contains no data that requires backup or migration.
Process in Short:
- Enter Maintenance Mode
- Remove Host from vDS Switches
- Unmount and Detach iSCSI LUNs
- Move host from cluster to datacenter as standalone host
- Remove Host from Inventory
Please read further for extended procedures and more information.
Enter Maintenance Mode
We enter maintenance mode to confirm that no VMs are running on the host. You can simply right click the host, and enter maintenance mode.
Remove Host from vDS Switches
You must gracefully remove the host from any vDS switches (VMware Distributed Switches) before removing the host from vCenter Server.
You can create a standard vSwitch and migrate vmk (VMware Kernel) adapters from the vDS switch to standard vSwitch, to maintain communication with the vCenter server and other networks.
Please Note: If you are using vDS switches for iSCSI connectivity, you must gracefully develop a plan to deal with this beforehand, either by unmounting/detaching the iSCSI LUNs on the vDS before removing the switch, or gracefully migrating the vmk adapters to a standard vSwitch, using MPIO to avoid losing connectivity during the process.
Unmount and Detach iSCSI LUNs
You can now proceed to unmount and detach iSCSI LUNs from the selected system:
- Unmount the iSCSI LUN(s) from the host
- Detach the iSCSI LUN(s) from the host
You will unmount only on the selected host to be decommissioned, and then detach the LUNs (again only on the host you are decommissioning).
Move Host from Cluster to Datacenter as standalone host
While this may not be required, I usually do this to let vSphere Cluster Services (HA/DRS) adjust for the host removal, and also deal with reconfiguration of the HA agent on the ESXi Host. You can simply move the host from the cluster to the parent datacenter level.
Remove Host from Inventory
Once the host has been moved and a moment or two have elapsed, you can now proceed to remove the host from inventory.
While the host is powered on and still connected to vCenter, right click on the host and choose “Remove from Inventory”. This will gracefully remove objects from vCenter, and also uninstall the HA agent from the ESXi host.
Host Repurposing
At this point, you can now log directly on to the ESXi host using the local root password, and shutdown the host.