The Problem
I run a Sophos UTM firewall appliance in my VMware vSphere environment and noticed the other day that I was getting warnings on the space used on the ESXi host for the thin-provisioned vmdk file for the guest VM. I thought “Hey, this is weird”, so I enabled SSH and logged in to check my volumes. Everything looked fine and my disk usage was great! So what gives?
After spending some more time troubleshooting and not finding much, I thought to myself “What if it’s not unmapping unused blocks from the vmdk to the host ESXi machine?”. What is unampping you ask? When files get deleted in a guest VM, the free blocks aren’t automatically “unmapped” and released back to the host hypervisor in some cases.
Two things need to happen:
- The guest VM has to release these blocks (notify the hypervisor that it’s not using them, making the vmdk smaller)
- The host has to reclaim these and issue the unmap command to the storage (freeing up the space on the SAN/storage itself)
On a side note: In ESXi 6.5 and when using VMFS version 6 (VMFS6), the datastores can be configured for automatic unmapping. You can still kick it off manually, but many administrators would prefer it to happen automatically in the background with low priority (low I/O).
Most of my guest VMs automatically do the first step (releasing the blocks back to the host). On Windows this occurs with the defrag utility which issues trim commands and “trims” the volumes. On linux this occurs with the fstrim command. All my guest VMs do this automatically with the exception being the Sophos UTM appliance.
The fix
First, a warning: Enable SSH on the Sophos UTM at your own risk. You need to know what you are doing, this also may pose a security risk and should be disabled once your are finished. You’ll need to “su” to root once you log in with the “loginuser” account.
This fix not only applies to the Sophos UTM, but most other linux based guest virtual machines.
Now to fix the issue, I used the “df” command which provides a list of the filesystems, their mount points, and storage free for those fileystems. I’ve included an example below (this wasn’t the full list):
hostname:/root # df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda6 5412452 2832960 2281512 56% /
udev 3059712 72 3059640 1% /dev
tmpfs 3059712 100 3059612 1% /dev/shm
/dev/sda1 338875 15755 301104 5% /boot
/dev/sda5 98447760 13659464 79513880 15% /var/storage
/dev/sda7 129002700 4624468 117474220 4% /var/log
/dev/sda8 5284460 274992 4717988 6% /tmp
/dev 3059712 72 3059640 1% /var/storage/chroot-clientlessvpn/dev
You’ll need to run the fstrim command on every mountpoint for file systems “/dev/sdaX” (X means you’ll be doing this for multiple mountpoints). In the example above, you’ll need to run it on “/”, “/boot”, “/var/storage”, “/var/log”, “/tmp”, and any other mountpoints that use “/dev/sdaX” filesytems.
Two examples:
fstrim / -v
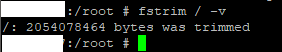
fstrim /var/storage -v
Again, you’ll repeat this for all mount points for your /dev/sdaX storage (X is replaced with the volume number). The command above only works with mountpoints, and not the actual device mappings.
Time to release the unused blocks to the SAN:
The above completes the first step of releasing the storage back to the host. Now you can either let the automatic unmap occur slowly overtime if you’re using VMFS6, or you can manually kick it off. I decided to manually kick it off using the steps I have listed at: https://www.stephenwagner.com/2017/02/07/vmfs-unmap-command-on-vsphere-6-5-with-vmfs-6-runs-repeatedly/
You’ll need to use esxcli to do this. I simply enabled SSH on my ESXi hosts temporarily.
Please note: Using the unmap command on ESXi hosts is very storage I/O intensive. Do this during maintenance window, or at a time of low I/O as this will perform MAJOR I/O on your hosts…
I issue the command (replace “DATASTORENAME” with the name of your datastore):
esxcli storage vmfs unmap --volume-label=DATASTORENAME --reclaim-unit=8
This could run for hours, possibly days depending on your “reclaim-unit” size (this is the block size of the unit you’re trying to reclaim from the VMFS file-system). In this example I choose 8, but most people do something larger like 100, or 200 to reduce the load and time for the command to complete (lower values look for smaller chunks of free space, so the command takes longer to execute).
I let this run for 2 hours on a 10TB datastore, however it may take way longer (possibly 6+ hours, to days).
Finally, not only are we are left with a smaller vmdk file, but we’ve released the space back to the SAN as well!
 VMware vSphere 6.7 Download Link
VMware vSphere 6.7 Download Link